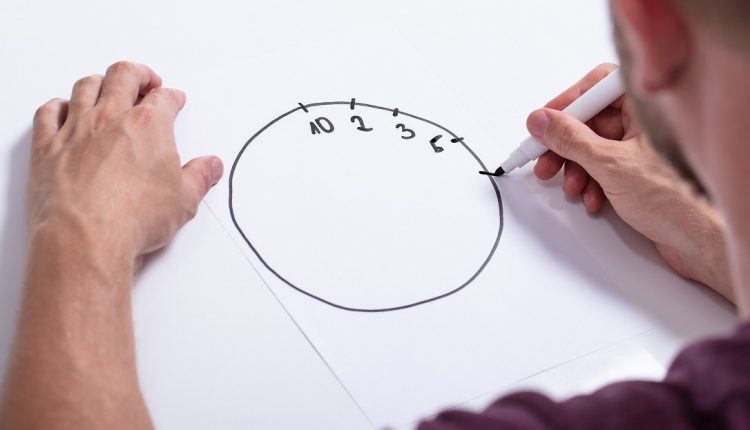
Clock Drawing Test for Alzheimer’s and Dementia
Healthcare professionals use the Clock Drawing Test to detect early signs of cognitive impairment, commonly referred to as the Alzheimer’s test or dementia test. The test is an indispensable clinical resource for detecting Alzheimer’s and dementia. This article will discuss the benefits and widespread use of the Clock Drawing Test in diagnosing these conditions.
Contents
What is the Clock Drawing Test?
The Clock Drawing Test is a cognitive assessment tool used to evaluate a person’s ability to draw a clock. The clock-drawing test is used to diagnose dementia in the early stages. One of the first signs of dementia is difficulty understanding what a clock’s hands represent.
In this Alzheimer’s test, the individual is asked to draw a clock face and set the hands to a specific time, typically 10 minutes past 11. This Alzheimer’s test is fast, easy to administer, and requires minimal resources, making it appropriate for many different clinical settings.
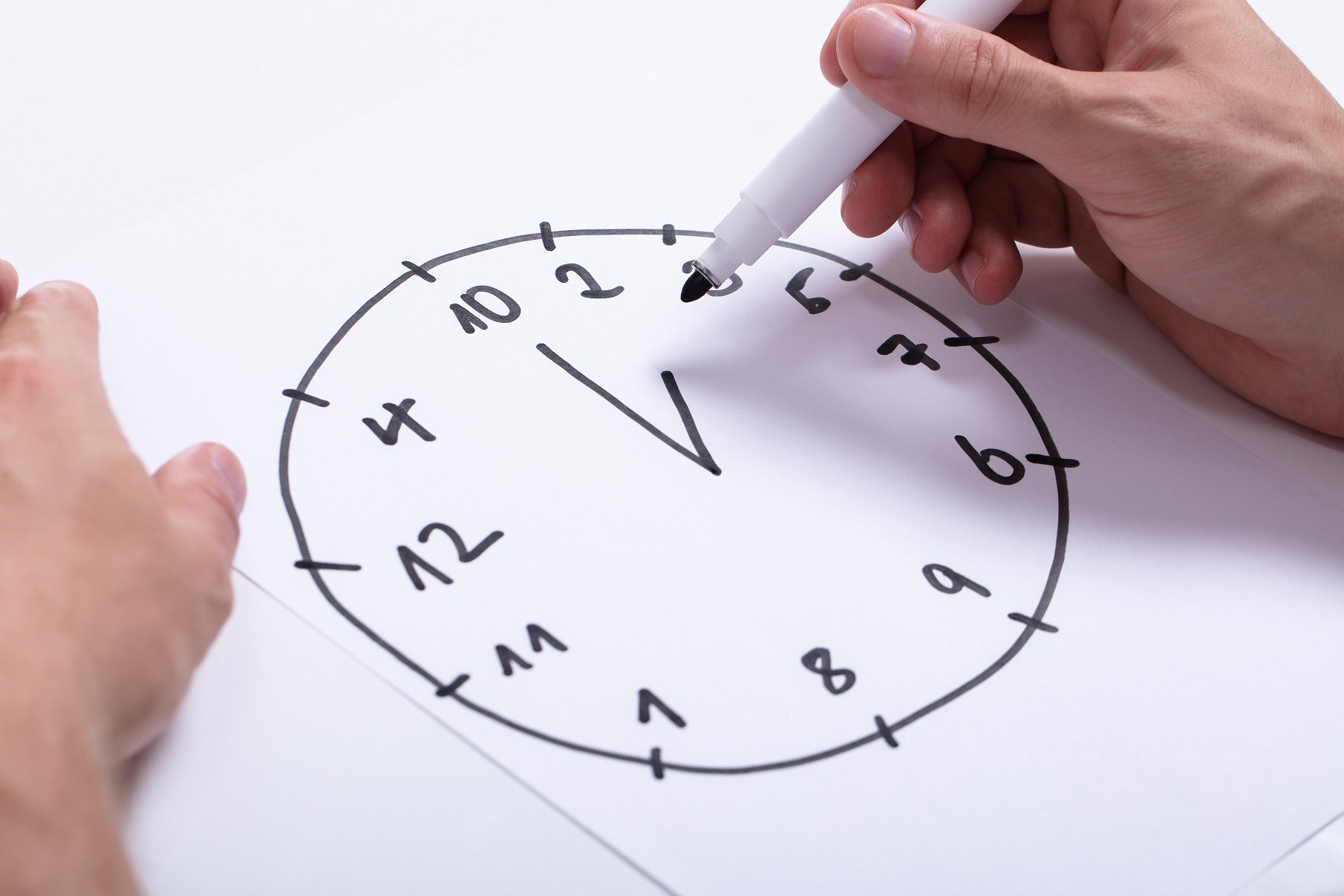
The Objectives of Alzheimer’s Test: Clock Drawing
Clock Drawing Tests are crucial in the early detection of Alzheimer’s and dementia. Healthcare professionals can detect cognitive decline in its earliest stages by analyzing an individual’s ability to draw a clock face and set the hands to a specific time.
This Alzheimer’s and dementia test determines whether an individual has any cognition loss. Cognition is the ability to learn, understand, and reason through experience, thoughts, and senses.
As people with dementia often have difficulty reading traditional clocks, the clock-drawing test can detect mental decline. It is necessary to interpret both the placement of the hands on a clock as well as the time they represent in order to read a clock. People with early dementia often lose this ability.
Clock Drawing Test Benefits
Alzheimer’s disease impacts many cognitive functions, including working memory, flexible thinking, and self-control. Furthermore, it affects motor programming, which refers to representing sequence and movement abstractly, as well as visual-spatial ability, which involves interpreting object relationships in space. Alzheimer’s disease also affects attention and concentration.
The task of drawing a clock involves all of these skills. If a person has difficulty completing the task, they may be suffering from dementia.
There is evidence that the clock-drawing test can detect early dementia even if other tests are normal, such as the mini-mental state exam (MMSE).
Early detection of Alzheimer’s and dementia is crucial as certain medications can slow the progression of the conditions. In this context, the clock-drawing test proves advantageous due to its speed and simplicity. Taking just a few minutes to complete, the dementia test only requires a pencil and paper. Administering it requires minimal training when utilizing a straightforward scoring method.
How to Do the Clock Drawing Test
A doctor or other qualified professional can administer the clock-drawing dementia test. All you need is a pencil and a piece of paper with a circle drawn on it.
First, the doctor will ask the patient to draw the numbers on the clock face.
In the next step, doctors will ask the person to draw the hands to show a specific time. While they can use different times for this task, many doctors opt for 10 minutes after 11.
This Alzheimer’s test can be modified by giving the subject a blank piece of paper and asking them to draw a clock showing 10 minutes after 11. In order to avoid giving clues, the word “hands” is not used. It is usually necessary to do three drawings within a set period of time.
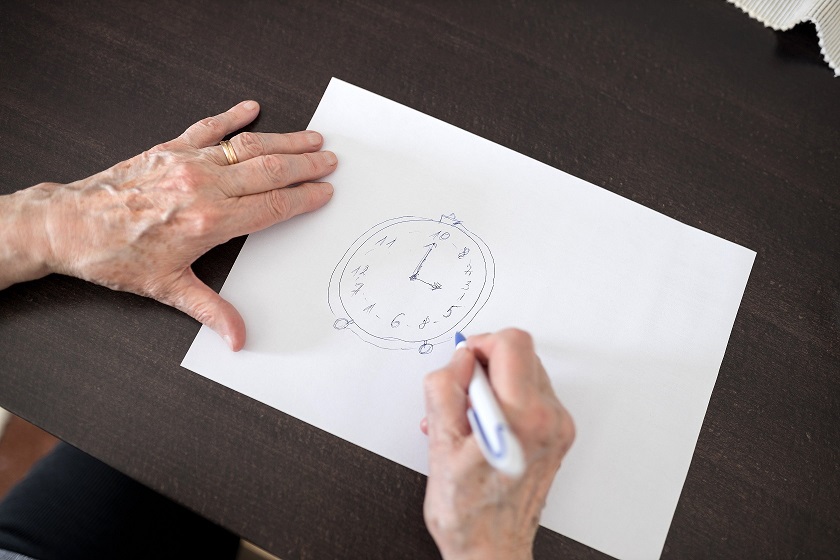

Scoring & Interpretation
It is possible to score the clock-drawing test in 15 different ways. Depending on whether or not the sequence of numbers, the placement of numbers, and the placement of the hands are correct; some methods can award 10, 15, or 20 points.
Missing numbers, missing hands, repeated numbers, the wrong sequence of numbers, or the incorrect time can also cause errors. The refusal to draw a clock can even indicate dementia.
The simplest scoring method gives one point for correct drawings and zero points for incorrect ones.
Limitations of Clock Drawing Test as Dementia Test
Besides several benefits this dementia test offers, it has its limitations. Clock drawing tests cannot diagnose the type of dementia. While this test can indicate early dementia, it cannot determine whether Alzheimer’s or another condition is present. It would be necessary to conduct other tests.
There is a possibility of misinterpretation. The tester may misdiagnose conditions like vascular dementia as Alzheimer’s if they are not a medical professional.
Final Words
The Clock Drawing Test is an effective and widely used tool for detecting and tracking Alzheimer’s disease and dementia. In addition to its simplicity, low cost, and cross-cultural applicability, it is a practical option for healthcare professionals who need to perform an Alzheimer’s test or a dementia test. However, healthcare professionals should use it in conjunction with other diagnostic methods to ensure an accurate and comprehensive evaluation. The Clock Drawing Test is likely to remain a fundamental tool in assessing cognitive impairment and providing timely treatment to those affected.
What other types of cognitive assessment tests are commonly used in clinical practice besides the Clock Drawing Test?
This reminds me of a tv series, in which the guy could not draw a clock due to some form of brain damage.