Free Cognitive Tests for Dementia
Dementia is a condition in which people lose a wide range of mental abilities, including memory, language, reasoning, and problem-solving. As these gradual changes intensify, they may affect a person’s daily life and relationships. Each year, doctors diagnose around ten million new cases of dementia. The cause and type of this condition can be challenging to determine since numerous diseases destroy the brain. It is, however, essential for a person to receive an early diagnosis of dementia to receive effective treatment and support for their future. This article explores the top free cognitive tests for dementia and free dementia tests that help you in early dementia diagnosis.
Contents
Who Needs a Cognitive Assessment?

As there is a difference between normal aging and dementia, natural age-related memory loss should not be a concern. However, a person should consult a healthcare provider if their cognitive symptoms or memory changes interfere with their daily lives.
The early signs and symptoms that can be a cause of concern are as follows:
- Not being able to remember appointments and important dates
- A loss of memory for familiar information
- Difficulty in performing everyday tasks
- Having a hard time remembering people’s names
- Being unable to remember whether a close family member is still alive
- Changes in personality
- Depression
- Falling
Free Cognitive Tests for Dementia
One of the ways doctors assess people with dementia is through cognitive tests. Free dementia tests determine if a person needs further evaluation and whether a full evaluation is necessary.
A cognitive test measures a variety of mental abilities, including:
- Awareness of people, time, and place
- Short- and long-term memory
- Communication and language skills
- Problem-solving
- Basic math skills
- Visual and spatial skills
- Concentration and attention
- Instruction-following ability
Most dementia tests are brief and involve verbal and written questions with corresponding scores.

1. Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA)
Healthcare providers use this 30-item test to assess a person’s thinking abilities. MoCa test assesses language, memory, visual and spatial thinking, reasoning, and orientation skills. The test consists of 30 questions that take 10–12 minutes to complete. According to doctors, people who score 26 and above do not have cognitive impairments. Researchers found that mild cognitive impairment patients scored an average of 22.1 while Alzheimer’s patients scored an average of 16.2.
2. Mini-Cog Test
The Mini-Cog test comprises a memory task involving the recall of three words and an evaluation of a clock drawing task.
Three-Word Recall
An administrator begins the test by reading three unrelated words in a loud voice to ensure the subject hears them correctly. Among the possible examples would be “banana, sun, chair” or “daughter, heaven, mountain.” Then, the test-taker is asked to draw a clock. Afterwards, the test-taker has to repeat the three words spoken at the beginning.
A three-word recall test measures short-term memory. Repeating these words after drawing the clock distracts memory, and the process will often prove too difficult for a person with Dementia in its early stages.
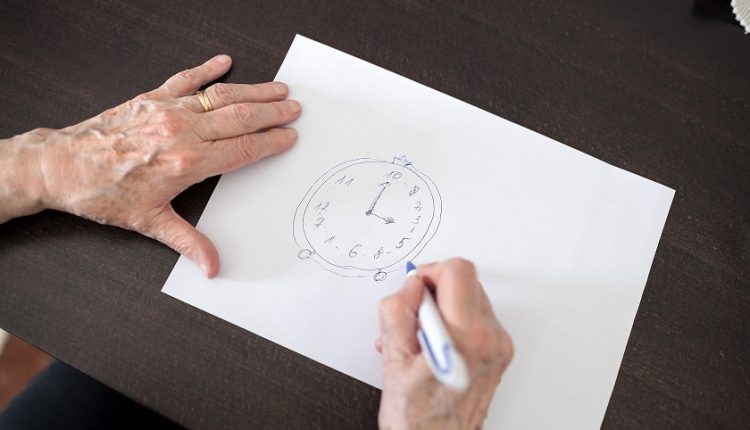
The Clock Drawing Test
The second part of the Mini-Cog is what the name suggests. Subjects should draw a clock showing a specific time, usually “10 past 11.” While this task seems simple, it is challenging for someone experiencing mild cognitive impairment or Dementia in its earliest stages.
This test evaluates different aspects of brain function:
– Verbal Understanding: Turning words (“Draw a clock”) into actions.
– Visual Memory: Visualizing what a clock looks like. Sadly, people with Dementia often struggle with this.
– Planning and Understanding: It takes multiple steps to draw a clock. The circle comes first; then, the numbers are written in the correct places, followed by the hands.

3. Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE)
MMSE is a screening test commonly used to identify cognitive impairments like dementia. The test consists of 11 questions or tasks grouped under seven “cognitive domains.” It can be completed in five minutes.
A person can score up to 30. A healthcare professional bases the score on direct observation of the person completing items or tasks. Doctors can score a person’s level of dementia based on their score:
- 25–30: no impairment
- 20–24: mild dementia
- 13–20: moderate dementia
- 12 and below: severe dementia
4. Sage Test for Dementia
SAGE test includes 12 questions covering memory, problem-solving, and language aspects of cognition.
The test is available in four different versions. While they’re similar, having multiple versions means it’s possible to take the test once a year and not get a higher score if subjects decide to retake it. Anyone can take the free SAGE test at any time.
Benefits of Early Detection
Diagnoses offer relief because they answer why a person’s memory is failing, their behaviour has changed, and they are having difficulty communicating.
People with dementia, and their loved ones, can plan for their future care, support, and treatment when they detect dementia. As a result, they have time to arrange legal and financial matters.
As well as preventing or slowing down the disease, doctors may recommend lifestyle changes. Furthermore, a formal diagnosis allows a person to receive treatments for symptoms, build a care team, and enroll in clinical trials.
Final Words
Dementia causes mental abilities to decline as brain cells die gradually. A cognitive assessment and dementia tests measure a person’s ability to think, such as memory, language, and reasoning. Like the list above, many of these cognitive tests can identify early cognitive impairment, which can help detect the early stages of dementia and people at risk of developing it. Moreover, they are free. Also, you can take these cognitive tests anytime and anywhere because usually, these tests are available online.