Can MRI Diagnose Alzheimer’s?
There has been a lot of debate recently about MRI and dementia. Can MRI diagnose Alzheimer’s? This is a complicated question. Let’s start by saying it can definitely be helpful in diagnosing the problem behind dementia. The word “Dementia” often begins to bubble up when a person develops cognitive deficits. This is typically observable by people who know the individual intimately, can judge their mental decline, and see how it interferes with their daily lives. However, such judgments do not suffice to diagnose dementia, and a number of clinical tests like an MRI must take place before we can be sure. Keep reading to discover more about MRI and dementia, MRI and Alzheimer’s.
Contents
A Brief Introduction to Dementia
Dementia is a general term for neurocognitive deficiencies that hinder the ability to live a normal life because of memory loss, decision-making difficulties, or concentration difficulties. The most well-known form of dementia is Alzheimer’s disease, and the second is “vascular dementia,” which is where an MRI diagnosis can be helpful.
The fact is, it is currently impossible to accurately diagnose any kind of dementia with a single test. First, one must understand how dementia works in order to understand how MRI fits into the diagnosis process.
Luckily, there is currently a lot of research going on to develop more accurate and earlier methods of diagnosing dementia, like the MRI scan. It is crucial to early diagnose dementia in order to plan treatment and maximize the chances of success.
MRI and Alzheimer’s
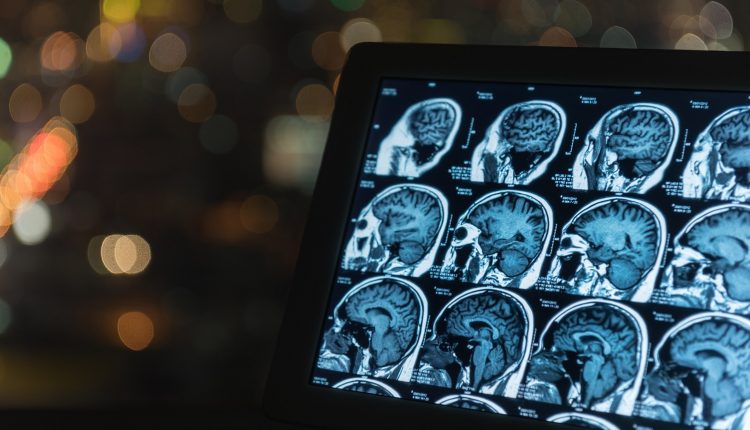
MRIs are high-resolution imaging tools used to detect structural abnormalities. MRI machines produce images by making loud banging noises as you lie on narrow tables that slide into tubes.
The procedure is painless, but some people find it claustrophobic, and the noise disturbs them. When it comes to strokes, ministrokes, abnormalities in blood vessels, and vascular dementia, MRIs are generally the preferred imaging test because they can provide even more information than CT scans.
Healthcare providers also order MRI studies to rule out physical abnormalities that could cause symptoms associated with dementia when they diagnose a patient with dementia. The size of different parts of the brain may decrease in the later stages of Alzheimer’s disease (primarily the temporal and parietal lobes). The results of a brain scan can help doctors diagnose strokes, tumours, and other problems that may contribute to dementia. Just remember, It is possible to have a normal brain MRI scan during the early stages of Alzheimer’s disease.
The Types of Brain Scans that Help Diagnose Dementia
The doctor will likely order blood work, a neurological examination, and imaging tests for your head as part of the medical exam. These tests include CT scans, PET/CT scans or MRIs to diagnose dementia. The majority of these are typical medical Tests for Seniors Over 60.
It is most common to perform a brain scan using computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Doctors frequently refer to CT or MRI scans of the brain when examining patients suspected of dementia. The MRI diagnoses Alzheimer’s by detecting hydrogen atoms in tissues within the body using magnetic fields and focused radio waves. CT scans can detect the same problems as MRIs, but MRIs can detect certain conditions more efficiently, including brain atrophy and subtle ischemia or stroke damage.
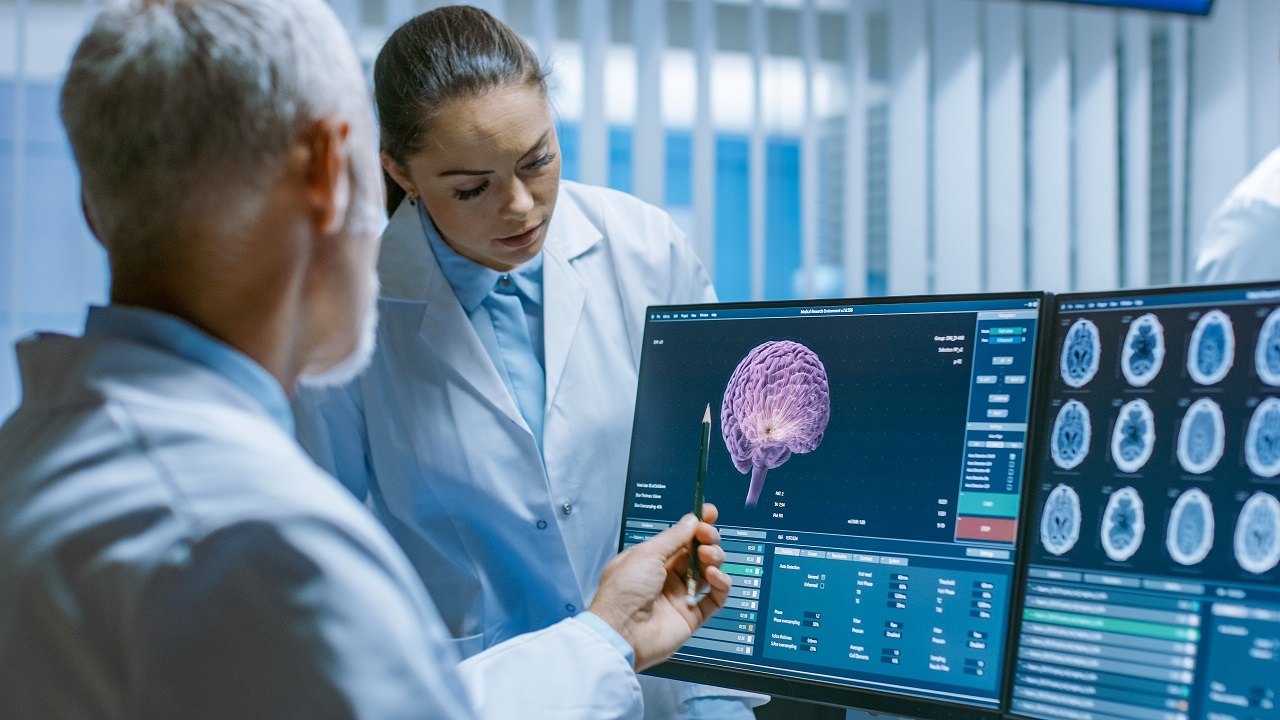

Is an MRI Scan a Good Way to Prevent Dementia?
Dementia cannot be prevented in a certain and scientifically proven way. There are, however, a number of risk factors that contribute to this condition, including:
- High blood pressure
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Lack of physical activity
- Poor diet
- High alcohol consumption
- Low levels of cognitive engagement
A brain scan using MRI or CT scan could be helpful in order to get ahead of the problem and detect certain conditions more efficiently.
Final Words
The diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease relies on identifying certain symptoms and excluding other possible causes. This is where an MRI scan can be helpful. When a patient exhibits memory loss, decision-making difficulties, or disorientation, they may be suffering from an organic disease process that can be treated to reduce or eliminate the symptoms. It is crucial to perform an MRI scan on a dementia patient in order to treat them effectively.
Is it possible for the things they inject before MIRs to cause allergies?
I have a fear of confined spaces. Whenever the doctor sent me for MRIs, I panicked and couldn’t bear it. The last thing I want is to have to check my brain for Alzheimer’s disease!